Memristors
 Memristor is a device which can be switched between high and low resistance states and which remembers that state until it is switched again. Memristors enable new kind of computers, which mimics the brain. This kind of neuromorphic computers are expected to be much more efficient in e.g. pattern recognition than traditional computers. Most of the working memristors are based on oxides and the atomic level working principles are still under investigation.
Memristor is a device which can be switched between high and low resistance states and which remembers that state until it is switched again. Memristors enable new kind of computers, which mimics the brain. This kind of neuromorphic computers are expected to be much more efficient in e.g. pattern recognition than traditional computers. Most of the working memristors are based on oxides and the atomic level working principles are still under investigation.
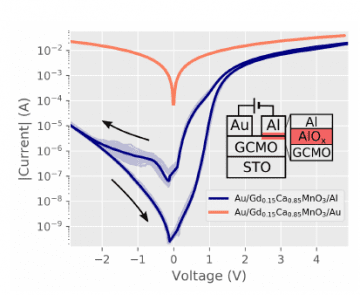
In Wihuri we have used a junction between perovskite strucured Gd1-xCaxMnO3 thin film and aluminum, which probably relies on the easy movement of oxygen atoms in the perovskite structure. Unlike in other manganite bases memristors, our Ca doping is around 0.9, where as in the most common Pr1-xCaxMnO3 memristors, concentration varies between 0.3 – 0.5. Our structures also enable almost analog control of the states instead of just high and low states, which is much closer to the workings of a synapse in the brain that the two lever switching.