Intelligent Control for Automated Insulin Delivery Systems
Check out our new paper on intelligent control for automated insulin delivery systems: [Link].
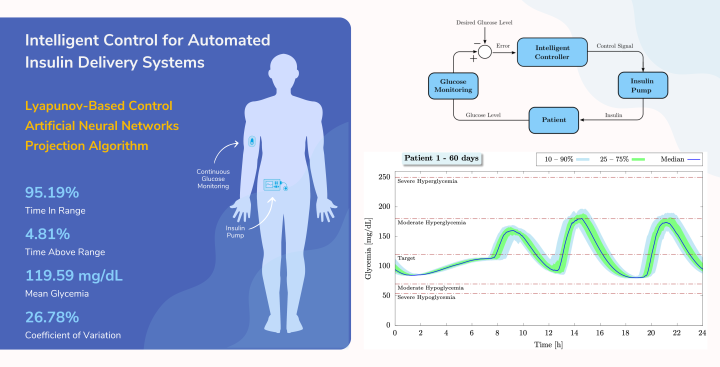
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin action, secretion, or both. For patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), modern therapy consists of continuous blood glucose monitoring (CGM) and automatic insulin delivery. By combining a CGM device with an insulin pump, it became possible to deploy automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, also known as an artificial pancreas. However, in addition to the insulin pump and the CGM sensor, an appropriate algorithm to automatically define the amount of insulin to be delivered to the patient is also a fundamental part of developing an effective artificial pancreas.
In this work, we introduce a novel intelligent controller for the automatic regulation of blood glucose levels. For this purpose, an artificial neural network (ANN) is incorporated in a Lyapunov-based nonlinear control law to ensure the stability of the closed-loop system. Online learning, instead of offline training, is proposed to update the ANN weights, which allows continuous learning and manages to cover all the nuances and variability of human physiology. The projection algorithm is employed to ensure that the ANN weights remain within predefined bounds, in order to avoid hypoglycemia due to insulin overdosing. By combining the artificial neural network with a non-linear control scheme, the computational demands on the ANN are drastically reduced. This in fact scales down the computational complexity of the algorithm and allows the proposed controller to be deployed on the low-power embedded hardware of automated insulin delivery systems. The efficacy of the proposed control scheme is evaluated through numerical simulations using the Identifiable Virtual Patient (IVP) model.