Review of 3D visualisations for communicative urban and landscape planning – we suggest a reporting framework for the heterogenous field
Salla Eilola, Department of Geography and Geology, University of Turku
In GreenPlace project together with colleagues from the University of Aalto, we conducted a literature review to better understand the current state of research on 3D visualization use in participatory planning. Our findings were just published in Landscape and Urban planning.
Public participation and collaboration supported by the opportunities that digital technologies offer are prolific themes in urban and landscape planning. In the past two decades, there has been a growing interest in the capacity of 3D visualisations to support citizen and stakeholder engagement in communicative planning processes. However, the technical advances of 3D visualisations still outstrip the current understanding of their benefits, appropriate uses and usability in practical planning contexts. There are no reviews or systematic mapping of literature, to our knowledge, that investigate the available evidence on the usability of particular 3D visualisations or that document the scope and gaps in current research on 3D applications in communicative planning. To answer this need we conducted a systematic mapping of academic literature reporting recent case studies of 3D visualisations that have been utilised or developed for communicative urban and landscape planning contexts.
We follow established guidelines for systematic reviews and used Scopus and Web of Science as primary electronic databases. Altogether, we reviewed 46 case studies globally. Our findings highlight the heterogeneity of planning contexts and purposes, terminology and technological 3D solutions. Moreover, the scarcity of real-life planning cases and robust and well-documented usability evaluations are evident in the literature. We discuss limitations of the existing academic literature for evidence-based understanding and suggest a common framework for reporting in the field of participatory and collaborative 3D visualisations to enable more rigorous and systematic evaluation of the usability and benefits of these technologies in urban and landscape planning.
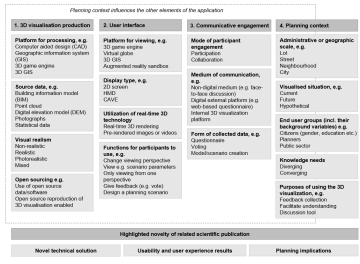
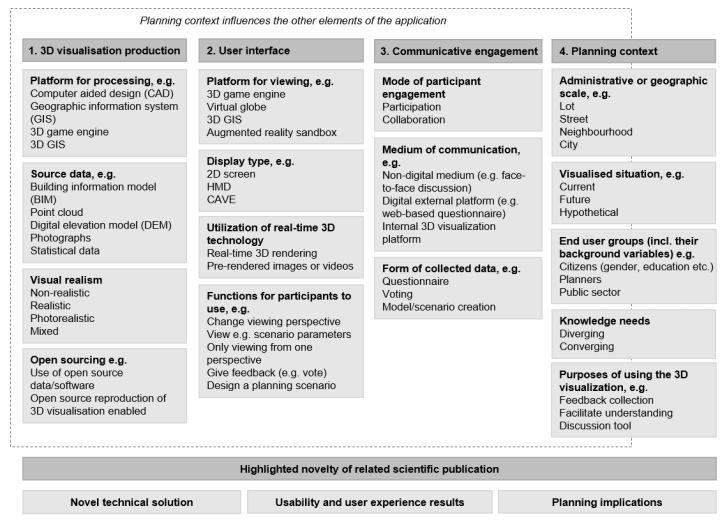
Figure. Framework for developing and reporting 3D visualisations for communicative urban and landscape planning.
We developed the four-category framework while analysing the reviewed literature to ensure that the technological solution and its application contexts would be comprehensively reported in a publication. It is meant for researchers, developers and planners to build a more comprehensive evidence base for evaluating the usability of 3D visualisations in communicative planning.
Eilola, S., Jaalama, K., Kangassalo, P., Nummi, P., Staffans, A., Fagerholm, N. (2023). 3D visualisations for communicative urban and landscape planning: What systematic mapping of academic literature can tell us of their potential? Landscape and Urban Planning, 234, 104716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2023.104716.