Research area
Safety culture and safety education in learning and working environments
Safety is considered from physical, psycho-social and pedagogical perspectives. Special interest focuses on learning environments in craft, design and technology education, especially on occupational safety and related issues. Got interested? See our publications here.

What is safety pedagogics?
The safety pedagogic point of view includes the structured learning environment, the people, the practical safety and security solutions made in the school as well as the curriculum that creates a cognitive and functional context for teachers´ actions.
The teoretical framework, contents, and environment of safety education. The values and attitudes are emphasized in the situation, where safety and security related knowledge and skills are taught. All these create the safety competence. The safety education should be implemented in the early pedagogics, through the comprehensive education, further to vocational or higher education.Enhanching the safety culture in schools means, not just theoretical background and attitude, but also ability to act. Therefore it is important to stress skills in safety pedagogics. Here the safety pedagogic point of view includes the structured learning environment, the people, the practical safety and security solutions made in the school as well as the curriculum that creates a cognitive and functional context for teachers´ actions. (Somerkoski 2013, 133−143; Lindfors 2013, 144−157.) The frameworks of safety pedagogics is described in the figure below.
The teoretical framework, contents, and environment of safety education. The values and attitudes are emphasized in the situation, where safety and security related knowledge and skills are taught. All these create the safety competence. The safety education should be implemented in the early pedagogics, through the comprehensive education, further to vocational or higher education.Enhanching the safety culture in schools means, not just theoretical background and attitude, but also ability to act. Therefore it is important to stress skills in safety pedagogics. Here the safety pedagogic point of view includes the structured learning environment, the people, the practical safety and security solutions made in the school as well as the curriculum that creates a cognitive and functional context for teachers´ actions. (Somerkoski 2013, 133−143; Lindfors 2013, 144−157.) The frameworks of safety pedagogics is described in the figure below.
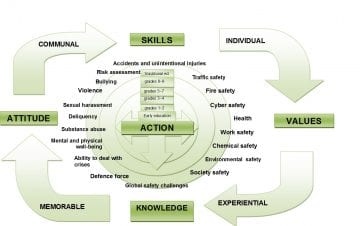
(Optuke 2012, Somerkoski 2015, modified in Lindfors & Somerkoski 2016)