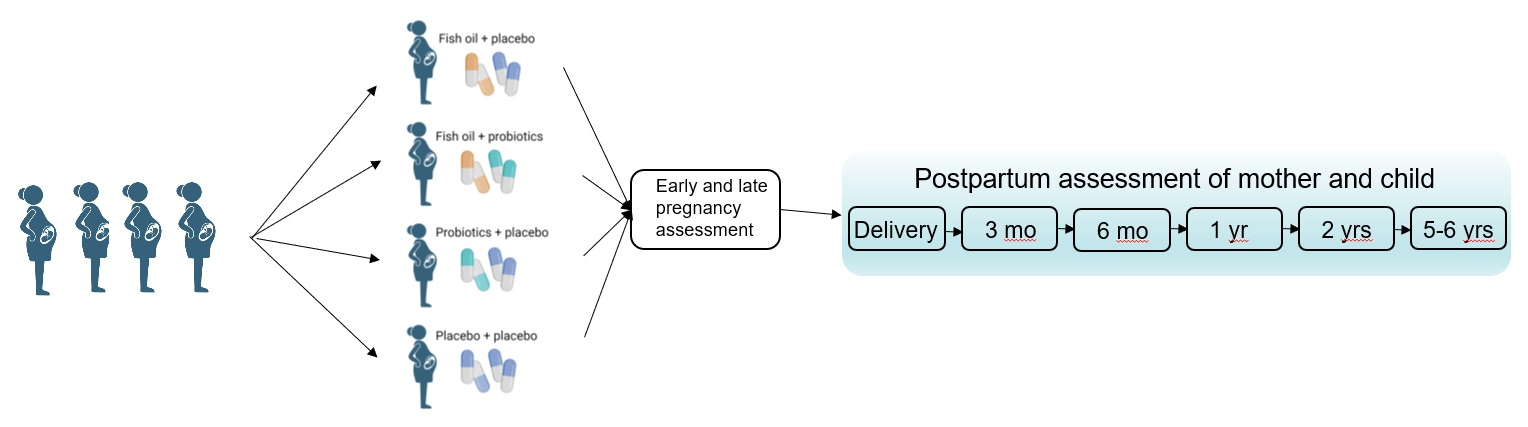
Fish Oil and Probiotics in Pregnancy (FOPP) study
FOPP, which stands for Fish Oil and Probiotics in Pregnancy, describes the focus of the study: fish oil and probiotics consumption by pregnant women and impacts on gut microbiota, metabolism and health of both the mother and the child. This clinical study began at the University of Turku and Turku University Hospital in the autumn of 2013, when women in early pregnancy were recruited, and the 5 to 6-year postpartum visits were completed in 2023.

The aims of the study are to determine whether probiotics and/or fish oil supplements can decrease the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus and to beneficially impact maternal weight and body composition during and after pregnancy. We are also investigating whether these supplements could influence the immune system of the child and thus potentially decrease the risk of allergy. Further, we study dietary intake, lipid metabolism, low-grade inflammation and gut and vaginal microbiota. In more general terms, this study will provide answers to how maternal diet should be modified in order to induce health benefits in both the mother and the child including the risk for glucose disorders and overweight. Also, the mechanisms of the underlying health effects will be enlightened. We also have an interest in food choice and eating behavior as determinants of dietary intake and health. Our study setup allows investigation of the long-term impacts of maternal nutrition during pregnancy on both maternal and child health. Further the impacts of child nutrition and metabolism on her/his own metabolic and clinical health as well as growth and development, including neurocognitive development are investigated.