Baltic herring
On these pages, you’ll find information on the spawning areas, spawning populations, reproductive success, and trap net fisheries of Baltic herring in the northern Baltic Sea. The texts are based extensively on research carried out by our group since the 1980s.
A keystone species in the ecosystem and a commercially valuable resource
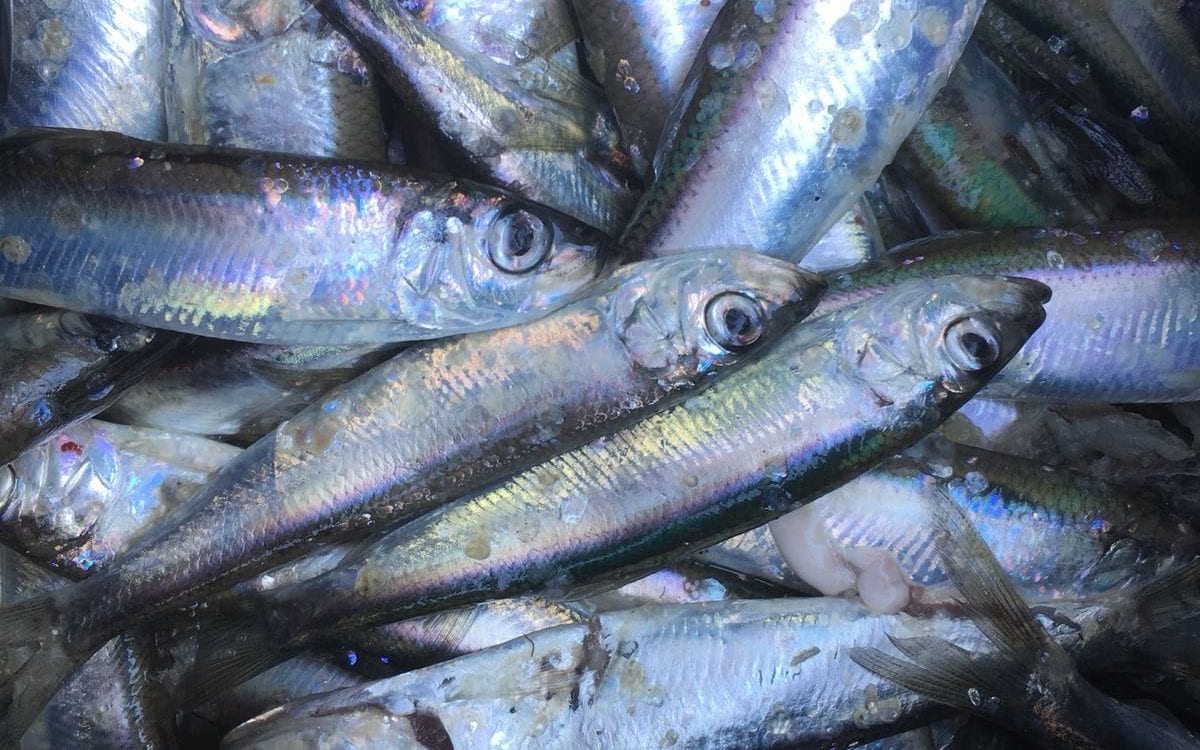
The Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) plays a pivotal role in the Baltic Sea’s ecosystem. It serves as a primary food source for predatory fish like Baltic cod and salmon, while also feeding on zooplankton and nektobenthos, contributing to the food web at multiple levels. With its high tolerance for varying salinity levels, Baltic herring is able to thrive and reproduce throughout nearly all areas of the Baltic Sea.
Despite fluctuations in abundance and biomass, Baltic herring has supported commercial fisheries for decades. In Finland, herring accounts for approximately 90% of the total marine fish catch by volume. It is the most commercially significant species, contributing around 17 million euros annually.
Spawning areas in the northern Baltic Archipelago Sea
The Archipelago Sea, located off Finland’s southwest coast, has been considered to be one of the largest primary spawning areas for Baltic herring along the Finnish coastline. This expansive coastal region, with over 40 000 islands, intricate coastlines, and shallow waters (averaging around 20 meters in depth), provides ideal spawning habitats. The area’s littoral zones are richly vegetated, hosting macroalgae such as Fucus, Cladophora, Enteromorpha, Pilayella, and Ectocarpus, along with vascular plants like Potamogeton and Ranunculus, and occasionally Zostera. Several rivers, including the Aurajoki, Mynäjoki, and Paimionjoki, flow into this region, forming sheltered and productive estuaries that enhance its suitability as a herring spawning ground.